23.08.2016
Capacitors – The Ultimate Guide
Published on: 23/08/2016
From the definition of a capacitor, to the meaning of capacitance, learn everything you need to know about capacitors with our ultimate guide.
.jpg)
What is a Capacitor?
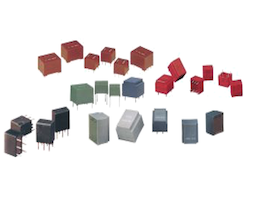
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component which is used to store an electrical charge. Each capacitor varies in appearance but all of them contain at least two conductors separated by a dielectric.
Along with semiconductors and heat sinks, capacitors are fundamental to commercial and industrial users of power electronic components. All power circuits rely heavily on capacitors for their ability to store local energy, complex signal filtering and voltage spike suppression.
Not all capacitors are equal, each capacitor has a different amount of capacitance. The capacitance value indicates how much charge the component can store. The value of the charge stored in a capacitor depends on the size of the capacitance, the larger the capacitance, the more charge it can store. The size of a capacitor is measured in units called farads, which is abbreviated F or microfarads in cases when the charge is smaller than a farad.
Capacitance
The capacitance (C) of the capacitor is equal to the electric charge (Q) divided by the voltage (V):

C is the capacitance in farad (F)
Q is the electric charge in coulombs (C), that is stored on the capacitor
V is the voltage between the capacitor’s plates in volts (V)
How does a Capacitor work?
The two metal plates and the insulating material (dielectric) are placed extremely close together in parallel with the dielectric placed in-between them to ensure they do not touch. Dielectrics are usually made out of: glass, paper, rubber, ceramic or plastic.

When the current flows in to the capacitor the charges get stuck on the plates because it cannot get past the insulating dielectric. This results in electrons being sucked in to one of the plates which causes it to be negatively charged. The remaining plate is left positively charged which forces both plates to be attracted to one another. The dielectric prevents the charges from connecting which causes the stationary charge on the plates to create an electric field which stores electric energy.

Types of Capacitors
AC Filter Capacitors
AC Filter Capacitors are specifically designed for traction inverter output filters, high power UPS input and output filters, multi-phase marine propulsion drives and specialised power factor correction.

Aluminum and Tantalum Electrolytic Capacitors
Electrolytic Capacitors are known for packing a lot of capacitance in to a relatively small volume. Commonly used in the range of 1µF-1mF, they are extremely well suited to high-voltage applications because of their high maximum voltage ratings. Aluminum electrolytic capacitors are one of the most popular types with both leads extending form the bottom.

Ceramic Capacitors
Ceramic Capacitors are the most commonly used and manufactured capacitor. They are made from a ceramic dielectric material and showcase a high voltage.

DC Filter Capacitors
A Decoupling Capacitor is used to suppress high-frequency noise in power supply signals. Propulsion and auxiliary inverters are used for railway traction, marine and avionic applications, static frequency converters and renewable energy systems for local & HVDC transmission

Energy Storage Capacitors
Energy Storage Capacitors are high-capacity electrochemical capacitors with greater capacitance values than other capacitors but has lower voltage limits. Applications include particle physics and plasma research, pulsed laser discharge, lithotripters, industrial and aviation turbine ignition.

Low Temperature Capacitors
Recently launched by GD Rectifiers and API, Low Temperature Capacitors can now be used across a wide temperature range from -55°C to +105°C.

Snubber Capacitors
Snubber Capacitors are used to suppress voltage transients in electrical systems, fluid systems or excess force or rapid movement in mechanical systems and pressure transients in fluid systems. Applications include Thyristor bridges for ac/dc conversion, active front end rectifiers, GTO and IGCT based inverters and high power IGBT applications.

Track Circuit Capacitors
Track Circuit Capacitors are typically used for high reliability, single and switched multi-element assemblies for AC resonant railway signaling applications.

Variable Capacitors
Variable Capacitors are less commonly known but produce a wide range of capacitances. They are a reliable alternative to variable resistors in tuning circuits and are used to tune a radio.

GD Rectifiers are the UK’s leading distributor for API capacitors. API is a UK based specialist manufacturer of custom and high specification capacitors, GD Rectifiers are today proud to announce the launch of API’s new low temperature electrolytic capacitor.
For further information on all API products click here or alternatively call our friendly sales team for a quote today on: 01444 243452.
Find out more about the latest GD Rectifiers product range here.