24.07.2017
Types of Electrical Fuses
Published on: 24/07/2017
Discover the types of electrical fuses on offer and find the right fuse for your application

What is a Fuse?
Fuses are a crucial part of circuit protection; they are used to break the circuit if a fault in an appliance causes too much current flow. Fuses are a safety device, they protect the wiring and the appliance itself, fuses contain a piece of wire that melts easily and switches off an appliance. If the current going through the fuse is too great, the wire heats up until it melts which results in the fuse blowing and breaks the circuit.
Replaceable fuses are inserted in a three-pin plug which connects the live pin of the plug to the live wire.
What Fuse do I need?
Finding the right fuse for your appliance is easy, you just need to know the voltage and the power of the appliance to calculate the current flowing through it. The current indicates which fuse to use for the desired appliance.
For example, if a laptop has a power of 900 watts and uses the UK mains voltage of 230 volts, then the calculation would be: I=P/V
I = 900/230
= 3.913amps
Fuses are colour coded for their ratings, a 3amp fuse is red, a 5amp fuse is black (or dark blue) and a 13amp fuse is brown.
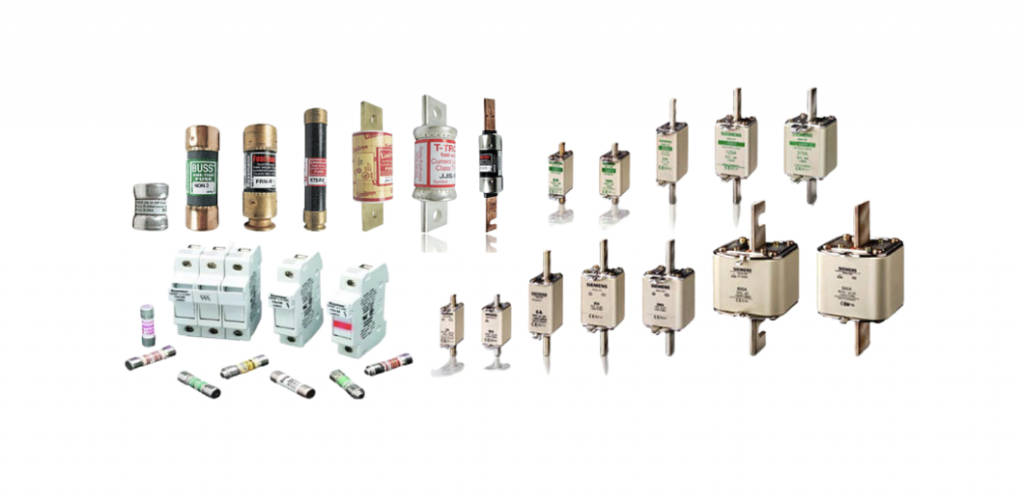
Types of Electrical Fuses
There are various different types of fuses available in the market used across both AC and DC circuits, discover some of the most well-known fuse types below:
AC and DC Fuses
There is little difference between AC and DC fuses.
One Time Only Fuses
One time use fuses contain a metallic wire which burns out when an overcurrent, overload or mismatched load connect event occur which results in the user needing to manually replace these fuses. One time use fuses are usually categorised by following:
Current carrying capacity of fuse – the amount of current which a fuse can easily conduct without interrupting the circuit.
Breaking capacity – the value of maximum current that can be safely interrupted by the fuse, this should be higher than the short circuit current.
I2t value of fuse – the amount of energy that carries the fuse element when the electrical fault is cleared
Response characteristic – the speed at which the blue blows, this depends on the amount of current flowing through its wire. The higher the current flowing through the wire the faster the response time will be.
Rated voltage of fuse – each fuse has a maximum allowed voltage rating, it is crucial to stick to these ratings. If a fuse is designed for 32 volts it cannot be used with 220 volts this is because different amounts of isolation is required in different fuses working on different voltage levels.
Packaging size – packaging sizes and types vary depending on the desired fuse, various applications require different packages to to be used accurately in the circuit. Packaging sizes and types are also dependent on: temperature derating, voltage drop and speed.
Cartridge Fuses
Cartridge fuses are used to protect electrical appliances such as motors air-conditions, refrigerator, pumps etc where high voltage rating and currents are required. Cartridge fuses are available up to 600A and 600V AC and are widely used in industrial, commercial and home distribution panels.
The two main types of Cartridge fuses are: General Purpose Fuses which have no time delay and Heavy Duty Cartridge Fuses with time delay. Both styles are available in 250V AC to 600V AC and its rating can be found on the end of the cap or knife blade.
Blade Type Fuses
Blade Fuses are predominantly used in automobiles for wiring and short circuit protection, they come in a plastic body and have two metal caps to fit in the socket.
Resettable Fuses
Resettable fuses can be used multiple times without replacing it. They are used to open the circuit when an over current event occurs. A resettable fuse is a passive component used to protect short current faults in electronic circuits. Resettable fuses can be used in most appliances, predominantly where manually replacing fuses is difficult or almost impossible to replace – such as nuclear or aerospace systems.
Medium Voltage Fuses
Medium voltage fuses generally fit into two categories – expulsion fuses and current limiting fuses.
Expulsion Fuses – limit the duration of an overcurrent event but do not limit the magnitude of fault current.
Current Limiting Fuses – reduce the magnitude a fault current as well as limit the duration of the overcurrent event when operating in its current limiting range. Current limiting fuses are for protection feeders, transformers and motor circuits designed to ANSI, BS, DIN and IEC standards.
UL Power Fuses
UL power fuses will provide a better overcurrent protection and minimise downtime and repair costs.
Fuse Applications
Electronic fuses are used in a wide range of electrical applications, some of these include:
- Motors
- Air conditions
- Home distribution boards
- General electrical applications
- Laptops
- Cell phones
- Game systems
- Printers
- Digital cameras
- DVD players
- Portable electronics
- LCD monitors
- Scanners
- Battery packs
- Hard disk drives
- Power converters
GD Rectifiers is the UK’s leading distributor of power Fuses and Microswitches. They work with three of the world’s leading manufacturers including, Eaton Bussmann (formerly known as Cooper Bussmann), Mersen (formerly known as Ferraz Shawmut) and IXYS UK Westcode (formerly known as Westcode).
Eaton Bussmann’s full range of fuses include: Low Voltage Fuses, British Style BS88 Fuses, Square Body Fuses, HV Fuses and much more. View the full product range here.
Mersen’s full range of fuses include: Ferrule-Style Fuses, NH Bladed Fuses, BS88 Low Voltage Fuses, Miniature Fuses and European Fuses. View the full product range here.
IXYS UK Westcode’s full range of fuses include: Ferrule-Style Fuses, NH Bladed Fuses, BS88 Low Voltage Fuses, Miniature Fuses and European Fuses. View the full product range here.
For further information on Fuses or to discuss how GD Rectifiers could help you, please call: 01444 243 452 or email: [email protected].