14.03.2022
Circuit Protection Devices used in the Medical Industry
Published on: 14/03/2022
Learn more about the broad range of circuit protection devices used in the medical industry today

Circuit protection options and components have developed significantly over the past 150 years which is largely due to the work of Edward V Sundt, Founder of what later became Littelfuse, when he patented the first small, fast-acting protective fuse in 1927.
As circuit protection technology has evolved over recent years, manufacturers now recognise a vast array of potential circuit failure modes and provide products to solve the wide range of circuit protection issues that can be found in battery-powered units as well those that are AC line powered.
Potential circuit failure modes
- Internal failures that can result in damage to other components
- Internal voltage or current operational issues that can cause stress to other components causing premature failure
- Current and voltage transients and spikes
Circuit Protection Devices
Thermal Fuses
Thermal fuses have many variations which must be taken into account when selecting the right fuse for your device. A thermal fuse uses a conducting fusible link that is fabricated of carefully selected metals with precise dimensions. Thermal fuses are designed to keep components safe in situations when an excessive temperature occurs.
PPTC Devices
PPTC devices provide increased resistance when overcurrent, overload or overtemperature is present which limits the power supply current, protecting circuit components.
MOVs
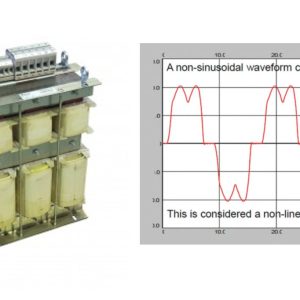
MOVs provide excellent transient suppression due to their sharp breakdown characteristics. MOVs are voltage dependent, non-linear devices that have similar properties to back-to-back Zener diodes.
TVS Diodes
Are a reliable form of high-voltage transient protection and are known for responding to overvoltage events faster than most other types of circuit protection devices.
Diode Arrays
Diode arrays help reduce capacitance seen by I/O lines due to their steering diodes centred around a large TVS diode.
SSRs
Solid state relays serve multiple objectives, they allow one voltage to switch and control an unrelated voltage with near-perfect galvanic isolation between input and output.
The most common function of a circuit protection device is to suppress large voltage transients. The two main types of transient suppressors include attenuate transients to prevent wide spreading into sensitive circuits and those that divert transients away by limiting the remaining voltage. It is crucial for buyers and engineers to study the device datasheets carefully, paying close attention to thermal and performance derating curves as some are often specified for transient protection which are bounded by voltage, current and time limits as opposed to steady-state protection.
Selecting the right fuse for a medical device can prove to be a complicated design challenge. There are often many suitable components to choose from but identifying the key attributes of each fuse and the requirements of the medical device is critical. No device will serve the multiple purpose of an array of circuit protection devices so designers need to consider multiple protection options. Designers should partner with distributors or application engineers to seek help in determining the most suitable fuse for their application, taking into consideration time to market, pricing, availability and planned maintenance or refurbishment schedules.
GD Rectifiers offers customers a wide range of circuit protection devices suited to the medical industry by having access to Littelfuse’s range of TVS Diodes, MOVs and Solid State Relays.
For further information on GD Rectifiers’ product range or to discuss your circuit protection requirements please call GD Rectifiers on 01444 243 452 or email: [email protected].